Are you a search pro? See below for details on how to use more advanced features to search the catalog, including Boolean search terms and details about search syntax.
Using Advanced Search
Quotation marks, Boolean searches, and other search syntax are available when using the default search toolbar, or "Basic Search." However, you can use "Advanced Search" to specify terms for multiple fields at once. Access Advanced Search below the search bar:
For example, consider a situation in which you want to quickly find a copy of the horror novel classic It by Stephen King.
Because the title of this novel, It , is a commonly used word, a basic title search will give many irrelevant results. This is a great opportunity to use "Advanced Search." You could use the following criteria:
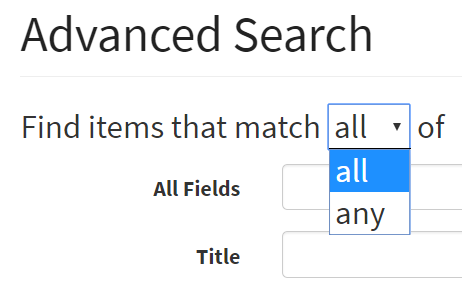
Find items that match all of:
- Title: It
- Author: Stephen King
- Resource Type: Book
The Advanced Search above returns only 3 results. The top result returns an available copy of the book.
In Advanced Search, you can specify whether the search should require ANY or ALL of the criteria:
Using Boolean search
You can conduct more sophisticated searches in both Basic and Advanced search using the Boolean operators AND , OR , NOT . Write the operators in all caps.
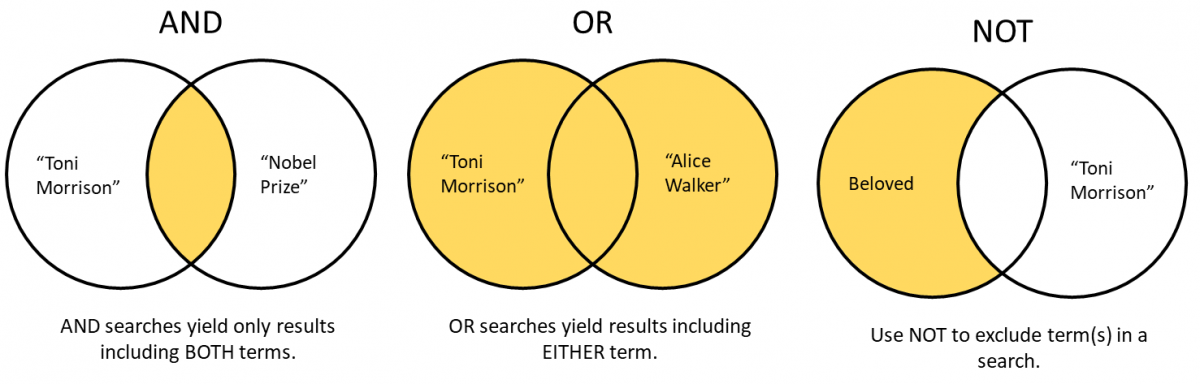
- AND
- Searches using AND yield results containing all of the search terms. Using AND has the effect of narrowing the search. For example, you could use "Toni Morrison" AND "Nobel Prize" to find Morrison's Nobel Prize acceptance speech.
- OR
- Searches using OR yield results including any of the search terms. Using OR has the effect of expanding the search. For example, you could find works by contemporary Black writers using "Toni Morrison" OR "Alice Walker."
- NOT
- Searches using NOT exclude the following term or parenthetical expression. For example, you could find items titled Beloved, while excluding work related to Toni Morrison, by using Beloved NOT "Toni Morrison" .
More tips about syntax
- Use quotation marks to search as a phrase, such as "Stranger in a Strange Land."
- The order of a name doesn't matter in a search. For example, John Fowles and Fowles, John will return the same results.
- In a search with 6 or fewer search terms and no Boolean operators, all of the search terms are required by default. Thus, searching climate change and climate AND change are equivalent.
- The example above does not require that the two terms be next to each other. To conduct a search for a phrase, use quotation marks (e.g. "climate change" ).
- Use parentheses to enclose a phrase, such as game NOT (chess OR checkers) .
- The Library Catalog is not case sensitive. Searches may be entered in any case. The only exception is that Boolean operators ( AND , OR , NOT ) should be capitalized.
Searching multiple library locations
It is possible to look for results that are available at one of several library locations. For example, you may be interested in items that are available at Perkins & Bostock or at Lilly Library.
On the Basic Search page, using facets to filter library locations will act as an AND search. For example, selecting Perkins & Bostock and Lilly will show results that are available at both Libraries, and exclude items that are available at only one.
To find items equivalent to the "Perkins & Bostock OR Lilly" search, use the Library Location attribute in Advanced Search.
